Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2016, 13(3), 294; doi:10.3390/ijerph13030294
Abstract
: Risk-behaviors are a major contributor to the leading causes of morbidity among adolescents and young people; however, their association with pathological Internet use (PIU) is relatively unexplored, particularly within the European context. The main objective of this study is to investigate the association between risk-behaviors and PIU in European adolescents. This cross-sectional study was conducted within the framework of the FP7 European Union project: Saving and Empowering Young Lives in Europe (SEYLE). Data on adolescents were collected from randomized schools within study sites across eleven European countries. PIU was measured using Young’s Diagnostic Questionnaire (YDQ). Risk-behaviors were assessed using questions procured from the Global School-Based Student Health Survey (GSHS). A total of 11,931 adolescents were included in the analyses: 43.4% male and 56.6% female (M/F: 5179/6752), with a mean age of 14.89 ± 0.87 years. Adolescents reporting poor sleeping habits and risk-taking actions showed the strongest associations with PIU, followed by tobacco use, poor nutrition and physical inactivity. Among adolescents in the PIU group, 89.9% were characterized as having multiple risk-behaviors. The significant association observed between PIU and risk-behaviors, combined with a high rate of co-occurrence, underlines the importance of considering PIU when screening, treating or preventing high-risk behaviors among adolescents.
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design and Population
2.2. Measurements
2.3. Individual Risk-Behaviors
2.3.1. Substance Use
2.3.2. Sensation-Seeking
2.3.3. Lifestyle Characteristics
2.4. Multiple Risk-Behaviors
3. Statistical Analyses
4. Results
4.1. Characteristics of the Study Sample
4.2. Prevalence of Risk-Behaviors

4.3. Multiple Risk-Behaviors
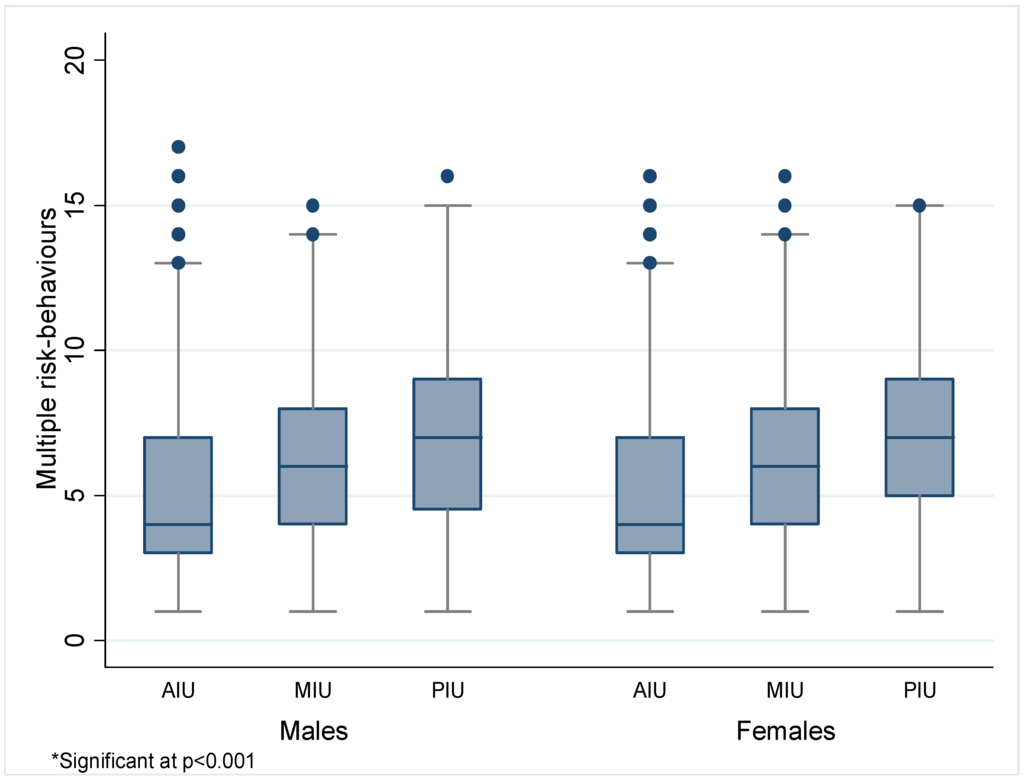

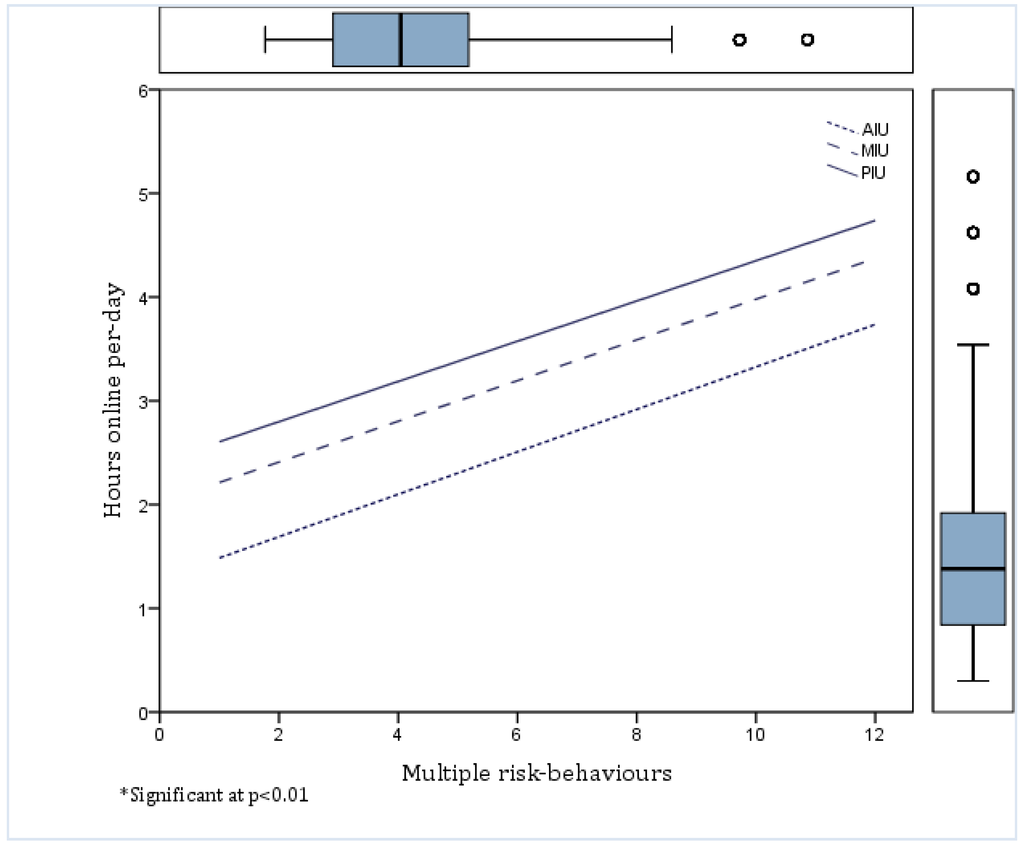
4.4. GLMM Analysis of the Association between Risk-Behaviors, MIU and PIU

4.5. Gender Interactions
5. Discussion
5.1. Prevalence of Risk-Behaviors
5.2. Substance Use
5.3. Sensation-Seeking
5.4. Lifestyle Characteristics
5.5. Multiple Risk-Behaviors
5.6. Gender Interactions
5.7. Griffiths’ Components Model
5.8. Strengths and Limitations
6. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| SEYLE | Saving and Empowering Young Lives in Europe |
| YRBSS | Youth Risk Behavior Surveillance System |
| GSHS | Global School-Based Student Health Survey |
| YDQ | Young’s Diagnostic Questionnaire |
| GLMM | Generalized linear mixed models |
| ANOVA | One-way analysis of variance |
| PIU | Pathological Internet use |
| MIU | Maladaptive Internet use |
| AIU | Adaptive Internet use |
| CI | Confidence intervals |
| SEM | Standard error of the mean |
| M | Mean |
References
- Moshman, D. Cognitive development beyond childhood. In Handbook of Child Psychology, 5th ed.; Kuhn, D., Damon, W., Siegler, R.S., Eds.; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 1998; Volume 2, pp. 947–978. [Google Scholar]
- Choudhury, S.; Blakemore, S.J.; Charman, T. Social cognitive development during adolescence. Soc. Cogn. Affect. Neurosci. 2006, 1, 165–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eccles, J.S.; Wigfield, A.; Byrnes, J. Cognitive development in adolescence. In Handbook of Psychology: Developmental Psychology; Lerner, R.M., Easterbrooks, M.A., Mistry, J., Eds.; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2003; Volume 6, pp. 325–350. [Google Scholar]
- Subrahmanyam, K.; Greenfield, P.; Kraut, R.; Gross, E. The impact of computer use on children’s and adolescents’ development. J. Appl. Dev. Psychol. 2001, 22, 7–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellison, N.B.; Steinfield, C.; Lampe, C. The benefits of Facebook “friends”: Social capital and college students’ use of online social network sites. J. Comput. Med. Commun. 2007, 12, 1143–1168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steinfield, C.; Ellison, N.B.; Lampe, C. Social capital, self-esteem, and use of online social network sites: A longitudinal analysis. J. Appl. Dev. Psychol. 2008, 29, 434–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tapscott, D. Growing up Digital: The Rise of the Net Generation; McGraw-Hill Education: New York, NY, USA, 2008; p. 384. [Google Scholar]
- Kraut, R.; Patterson, M.; Lundmark, V.; Kiesler, S.; Mukopadhyay, T.; Scherlis, W. Internet paradox. A social technology that reduces social involvement and psychological well-being? Am. Psychol. 1998, 53, 1017–1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kraut, R.; Kiesler, S.; Boneva, B.; Cummings, J.; Helgeson, V.; Crawford, A. Internet paradox revisited. J. Soc. Issues 2002, 58, 49–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, N.H.; Hillygus, D.S.; Erbring, L. Internet use, interpersonal relations, and sociability: A time diary study. In The Internet in Everyday Life; Wellman, B., Haythornthwaite, C., Eds.; Blackwell Publishers Ltd.: Oxford, UK, 2002; pp. 213–243. [Google Scholar]
- Nalwa, K.; Anand, A.P. Internet addiction in students: A cause of concern. Cyberpsychol. Behav. 2003, 6, 653–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akhter, N. Relationship between internet addiction and academic performance among university undergraduates. Edu. Res. Rev. 2013, 8, 1793. [Google Scholar]
- Gür, K.; Yurt, S.; Bulduk, S.; Atagöz, S. Internet addiction and physical and psychosocial behavior problems among rural secondary school students. Nurs. Health Sci. 2015, 17, 331–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peltzer, K.; Pengpid, S.; Apidechkul, T. Heavy internet use and its associations with health risk and health-promoting behaviours among Thai university students. Int. J. Adolesc. Med. Health 2014, 26, 187–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Punamaki, R.L.; Wallenius, M.; Nygard, C.H.; Saarni, L.; Rimpela, A. Use of information and communication technology (ICT) and perceived health in adolescence: The role of sleeping habits and waking-time tiredness. J. Adolesc. 2007, 30, 569–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Straker, L.; Pollock, C.; Maslen, B. Principles for the wise use of computers by children. Ergonomics 2009, 52, 1386–1401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shaw, M.; Black, D.W. Internet addiction: Definition, assessment, epidemiology and clinical management. CNS Drugs 2008, 22, 353–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Young, K. Internet addiction: The emergence of a new clinical disorder. CyberPsychol. Behav. 1998, 1, 237–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- American Psychiatric Association (APA). Diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders. Available online: http://www.dsm5.org (accessed on 2 February 2016).
- Petry, N.M.; O’Brien, C.P. Internet gaming disorder and the DSM-5. Addiction 2013, 108, 1186–1187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sussman, S.; Lisha, N.; Griffiths, M. Prevalence of the addictions: A problem of the majority or the minority? Eval. Health Prof. 2011, 34, 3–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, H.W.; Choi, J.S.; Shin, Y.C.; Lee, J.Y.; Jung, H.Y.; Kwon, J.S. Impulsivity in internet addiction: A comparison with pathological gambling. Cyberpsychol. Behav. Soc. Netw. 2012, 15, 373–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tonioni, F.; Mazza, M.; Autullo, G.; Cappelluti, R.; Catalano, V.; Marano, G.; Fiumana, V.; Moschetti, C.; Alimonti, F.; Luciani, M. Is internet addiction a psychopathological condition distinct from pathological gambling? Addict. Behav. 2014, 39, 1052–1056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sajeev Kumar, P.; Prasad, N.; Raj, Z.; Abraham, A. Internet addiction and substance use disorders in adolescent students-a cross sectional study. J. Int. Med. Dent. 2015, 2, 172–179. [Google Scholar]
- Brezing, C.; Derevensky, J.L.; Potenza, M.N. Non-substance-addictive behaviors in youth: Pathological gambling and problematic internet use. Child Adoles. Psychiatr. Clin. N. Am. 2010, 19, 625–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goldstein, R.Z.; Volkow, N.D. Dysfunction of the prefrontal cortex in addiction: Neuroimaging findings and clinical implications. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2011, 12, 652–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Montag, C.; Kirsch, P.; Sauer, C.; Markett, S.; Reuter, M. The role of the chrna4 gene in internet addiction: A case-control study. J. Addict. Med. 2012, 6, 191–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kormas, G.; Critselis, E.; Janikian, M.; Kafetzis, D.; Tsitsika, A. Risk factors and psychosocial characteristics of potential problematic and problematic internet use among adolescents: A cross-sectional study. BMC Public Health 2011, 11, 595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Y.; Lin, F.-C.; Du, Y.-S.; Zhao, Z.-M.; Xu, J.-R.; Lei, H. Gray matter abnormalities in internet addiction: A voxel-based morphometry study. Eur. J. Radiol. 2011, 79, 92–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Griffiths, M. A “components” model of addiction within a biopsychosocial framework. J. Subst. Use 2005, 10, 191–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, C.; Li, A.Y. Internet addiction prevalence and quality of (real) life: A meta-analysis of 31 nations across seven world regions. Cyberpsychol. Behav. Soc. Netw. 2014, 17, 755–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blinka, L.; Škařupová, K.; Ševčíková, A.; Wölfling, K.; Müller, K.W.; Dreier, M. Excessive internet use in European adolescents: What determines differences in severity? Int. J. Public Health 2015, 60, 249–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsitsika, A.; Janikian, M.; Schoenmakers, T.M.; Tzavela, E.C.; Ólafsson, K.; Wójcik, S.; Florian Macarie, G.; Tzavara, C.; Richardson, C. Internet addictive behavior in adolescence: A cross-sectional study in seven European countries. Cyberpsychol. Behav. Soc. Netw. 2014, 17, 528–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Durkee, T.; Kaess, M.; Carli, V.; Parzer, P.; Wasserman, C.; Floderus, B.; Apter, A.; Balazs, J.; Barzilay, S.; Bobes, J.; et al. Prevalence of pathological internet use among adolescents in Europe: Demographic and social factors. Addiction 2012, 107, 2210–2222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuss, D.J.; Griffiths, M.D.; Karila, L.; Billieux, J. Internet addiction: A systematic review of epidemiological research for the last decade. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2014, 20, 4026–4052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carli, V.; Durkee, T.; Wasserman, D.; Hadlaczky, G.; Despalins, R.; Kramarz, E.; Wasserman, C.; Sarchiapone, M.; Hoven, C.W.; Brunner, R.; et al. The association between pathological internet use and comorbid psychopathology: A systematic review. Psychopathology 2013, 46, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ho, R.C.; Zhang, M.W.; Tsang, T.Y.; Toh, A.H.; Pan, F.; Lu, Y.; Cheng, C.; Yip, P.S.; Lam, L.T.; Lai, C.-M.; et al. The association between internet addiction and psychiatric co-morbidity: A meta-analysis. BMC Psychiatry 2014, 14, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaess, M.; Durkee, T.; Brunner, R.; Carli, V.; Parzer, P.; Wasserman, C.; Sarchiapone, M.; Hoven, C.; Apter, A.; Balazs, J.; et al. Pathological internet use among European adolescents: Psychopathology and self-destructive behaviours. Eur. Child Adolesc. Psychiatry 2014, 23, 1093–1102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pontes, H.M.; Kuss, D.J.; Griffiths, M.D. The clinical psychology of internet addiction: A review of its conceptualization, prevalence, neuronal processes, and implications for treatment. Neurosci. Neuroeconomics 2015, 4, 11–23. [Google Scholar]
- Kipping, R.R.; Campbell, R.M.; MacArthur, G.J.; Gunnell, D.J.; Hickman, M. Multiple risk behaviour in adolescence. J. Public Health 2012, 34, i1–i2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dodd, L.J.; Al-Nakeeb, Y.; Nevill, A.; Forshaw, M.J. Lifestyle risk factors of students: A cluster analytical approach. Prev. Med. 2010, 51, 73–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berk, M.; Sarris, J.; Coulson, C.; Jacka, F. Lifestyle management of unipolar depression. Acta Psychiatr. Scand. 2013, 127, 38–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prochaska, J.J.; Spring, B.; Nigg, C.R. Multiple health behavior change research: An introduction and overview. Prev. Med. 2008, 46, 181–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carli, V.; Hoven, C.W.; Wasserman, C.; Chiesa, F.; Guffanti, G.; Sarchiapone, M.; Apter, A.; Balazs, J.; Brunner, R.; Corcoran, P. A newly identified group of adolescents at “invisible” risk for psychopathology and suicidal behavior: Findings from the SEYLE study. World Psychiatry 2014, 13, 78–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kann, L.; Kinchen, S.; Shanklin, S.L.; Flint, K.H.; Kawkins, J.; Harris, W.A.; Lowry, R.; Olsen, E.; McManus, T.; Chyen, D. Youth risk behavior surveillance—United States, 2013. MMWR Surveill. Summ. 2014, 63, 1–168. [Google Scholar]
- Wasserman, D.; Carli, V.; Wasserman, C.; Apter, A.; Balazs, J.; Bobes, J.; Bracale, R.; Brunner, R.; Bursztein-Lipsicas, C.; Corcoran, P.; et al. Saving and empowering young lives in Europe (SEYLE): A randomized controlled trial. BMC Public Health 2010, 10, 192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carli, V.; Wasserman, C.; Wasserman, D.; Sarchiapone, M.; Apter, A.; Balazs, J.; Bobes, J.; Brunner, R.; Corcoran, P.; Cosman, D. The saving and empowering young lives in Europe (SEYLE) randomized controlled trial (RCT): Methodological issues and participant characteristics. BMC Public Health 2013, 13, 479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Young, K.S. Caught in the Net: How to Recognize the Signs of Internet Addiction–and a Winning Strategy for Recovery; J. Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 1998; p. 248. [Google Scholar]
- Dowling, N.A.; Quirk, K.L. Screening for internet dependence: Do the proposed diagnostic criteria differentiate normal from dependent internet use? Cyberpsychol. Behav. 2009, 12, 21–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, W.; O’Brien, J.E.; Snyder, S.M.; Howard, M.O. Diagnostic criteria for problematic internet use among U.S. University students: A mixed-methods evaluation. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0145981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pontes, H.M.; Király, O.; Demetrovics, Z.; Griffiths, M.D. The conceptualisation and measurement of dsm-5 internet gaming disorder: The development of the IGD-20 test. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e110137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- World Health Organization (WHO). Global School-Based Student Health Survey (GSHS). Available online: http://www.who.int/chp/gshs/en/ (accessed on 12 December 2015).
- Choi, K.; Son, H.; Park, M.; Han, J.; Kim, K.; Lee, B.; Gwak, H. Internet overuse and excessive daytime sleepiness in adolescents. Psychiatry Clin. Neurosci. 2009, 63, 455–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Evren, C.; Dalbudak, E.; Evren, B.; Demirci, A.C. High risk of internet addiction and its relationship with lifetime substance use, psychological and behavioral problems among 10th grade adolescents. Psychiatria Danub. 2014, 26, 330–339. [Google Scholar]
- International telecommunication union (ITU). ICT Facts and Figures. Available online: http://www.itu.int/en (accessed on 8 August 2015).
- De La Haye, K.; D’Amico, E.J.; Miles, J.N.; Ewing, B.; Tucker, J.S. Covariance among multiple health risk behaviors in adolescents. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e98141. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, F.; Su, L.; Liu, T.; Gao, X. The relationship between impulsivity and internet addiction in a sample of Chinese adolescents. Eur. Psychiatry: J. Assoc. Eur. Psychiatr. 2007, 22, 466–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Slater, M.D. Alienation, aggression, and sensation seeking as predictors of adolescent use of violent film, computer, and website content. J. Commun. 2003, 53, 105–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.K.; Davis, K.E. Toward a comprehensive theory of problematic internet use: Evaluating the role of self-esteem, anxiety, flow, and the self-rated importance of internet activities. Comput. Hum. Behav. 2009, 25, 490–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charlton, J.P.; Danforth, I.D. Distinguishing addiction and high engagement in the context of online game playing. Comput. Hum. Behav. 2007, 23, 1531–1548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuss, D.J.; Griffiths, M.D. Online social networking and addiction—A review of the psychological literature. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2011, 8, 3528–3552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meena, P.S.; Mittal, P.K.; Solanki, R.K. Problematic use of social networking sites among urban school going teenagers. Ind. Psychiatry J. 2012, 21, 94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, W.; O’Brien, J.E.; Snyder, S.M.; Howard, M.O. Characteristics of internet addiction/pathological internet use in U.S. University students: A qualitative-method investigation. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0117372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lam, L. Internet gaming addiction, problematic use of the internet, and sleep problems: A systematic review. Curr. Psychiatry Rep. 2014, 16, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cain, N.; Gradisar, M. Electronic media use and sleep in school-aged children and adolescents: A review. Sleep Med. 2010, 11, 735–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hochadel, J.; Frolich, J.; Wiater, A.; Lehmkuhl, G.; Fricke-Oerkermann, L. Prevalence of sleep problems and relationship between sleep problems and school refusal behavior in school-aged children in children’s and parents’ ratings. Psychopathology 2014, 47, 119–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, S.S.J.; Tsai, C.C. Sensation seeking and internet dependence of Taiwanese high school adolescents. Comput. Hum. Behav. 2002, 18, 411–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsi-Peng, L.; Shu-ming, W. The role of internet addiction in online game loyalty: An exploratory study. Internet Res. 2008, 18, 499–519. [Google Scholar]
- Jessor, R.; Jessor, S.L. Problem Behavior and Psychosocial Development: A Longitudinal Study of Youth; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1977; p. 281. [Google Scholar]
- Jessor, R. Problem-behavior theory, psychosocial development, and adolescent problem drinking. Br. J. Addict. 1987, 82, 331–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Williams, J.H.; Ayers, C.D.; Abbott, R.D.; Hawkins, J.D.; Catalano, R.F. Structural equivalence of involvement in problem behavior by adolescents across racial groups using multiple group confirmatory factor analysis. Soc. Work Res. 1996, 20, 168–177. [Google Scholar]
- Ha, Y.-M.; Hwang, W.J. Gender differences in internet addiction associated with psychological health indicators among adolescents using a national web-based survey. Int. J. Ment. Health Addict. 2014, 12, 660–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuss, D.J.; Shorter, G.W.; van Rooij, A.J.; Griffiths, M.D.; Schoenmakers, T.M. Assessing internet addiction using the parsimonious internet addiction components model—A preliminary study. Int. J. Ment. Health Addict. 2014, 12, 351–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons by Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).