In this section we look at the studies linking porn use or porn addiction to sexual dysfunctions and lower arousal.
The first 6 studies linking porn use or porn addiction to sexual dysfunctions and lower arousal demonstrate causation. The participants eliminated porn use and healed chronic sexual dysfunctions:
1) Is Internet Pornography Causing Sexual Dysfunctions? A Review with Clinical Reports (2016) – An extensive review of the literature related to porn-induced sexual problems. Involving 7 US Navy doctors, the review provides the latest data revealing a tremendous rise in youthful sexual problems. It also reviews the neurological studies related to porn addiction and sexual conditioning via Internet porn. The doctors provide 3 clinical reports of men who developed porn-induced sexual dysfunctions. Two of the three men healed their sexual dysfunctions by eliminating porn use. The third man experienced little improvement as he was unable to abstain from porn use.
Description of the intervention for the 3 men:
While correlation studies are easier to conduct, the difficulty in isolating the precise variables at work in the unprecedented rise of sexual dysfunction in men under 40 suggests that intervention studies (in which subjects removed the variable of Internet pornography use) would better establish whether there is a connection between its use and sexual difficulties. The following clinical reports demonstrate how asking patients with diverse and otherwise unexplained dysfunctions to eradicate Internet pornography use helps to isolate its effects on sexual difficulties. Below we report on three active duty servicemen. Two saw a physician for their non-organic erectile dysfunction, low sexual desire, and unexplained difficulty in achieving orgasm with partners.
Excerpt describes assessment:
Our review and clinical reports also highlight the need for validated screening tools to identify the possible presence of non-organic sexual difficulties, as well as Internet pornography-related difficulties in otherwise healthy men. The latter may often be reversible simply by modifying behavior. Because Internet pornography-related sexual difficulties are not yet specifically encompassed in an official diagnosis, healthcare providers do not routinely screen for them, leaving patients vulnerable.
In this regard, in order to assess patients correctly, it may be critical to distinguish pornography-free from pornography-assisted masturbation. Traditionally, if patients had no difficulty with erections, arousal and climax while masturbating, but reported problems during partnered sex, they were presumed to have psychogenic, not organic, problems. However, young patients asked about their capabilities may assume “masturbation” refers to “masturbation with the aid of internet pornography”, and therefore be assessed as having “performance anxiety”, when their partnered-sex difficulties are actually Internet pornography-related.
One simple test healthcare providers might employ is to ask, “whether the patient can achieve and sustain a satisfactory erection (and climax as desired) when masturbating without using Internet pornography”. If he cannot, but can easily achieve these goals with Internet pornography, then his sexual dysfunction may be associated with its use. Without employing such a test, there is a risk of false diagnoses of “performance anxiety”, and a consequent risk of prescribing needless psychoactive medications and (ultimately perhaps ineffective) phosphodiesterase-5 inhibitors. Other indications of Internet pornography-related performance difficulties may be loss of nocturnal erections and/or spontaneous erections. Additional research in this area is warranted.
2) Male masturbation habits and sexual dysfunctions (2016) – The paper revolves around his clinical experience with 35 men who developed erectile dysfunction and/or anorgasmia, and the author’s therapeutic approaches to help them. The author states that most of his patients used porn, with several being addicted to porn. 19 of the 35 men saw significant improvements in sexual functioning. The other men either dropped out of treatment or are still trying to recover. Excerpts:
Intro: Harmless and even helpful in his usual form widely practiced, masturbation in its excessive and pre-eminent form, generally associated today to pornographic addiction, is too often overlooked in the clinical assessment of sexual dysfunction it can induce.
Results: Initial results for these patients, after treatment to “unlearn” their masturbatory habits and their often associated addiction to pornography, are encouraging and promising. A reduction in symptoms was obtained in 19 patients out of 35. The dysfunctions regressed and these patients were able to enjoy satisfactory sexual activity.
Conclusion: Addictive masturbation, often accompanied by a dependency on cyber-pornography, has been seen to play a role in the etiology of certain types of erectile dysfunction or coital anejaculation. It is important to systematically identify the presence of these habits rather than conduct a diagnosis by elimination, in order to include habit-breaking deconditioning techniques in managing these dysfunctions.
More on intervention:
Ten subjects had coital anejaculation, 25 subjects had erectile dysfunction. Of these, 5 cases showed both dysfunctions, 8 were also addicted to pornography and 8 also complained a significant decrease of libido. Biopsychosocial-Relational assessment did not find other potentially significant etiological factors, we chose addiction to masturbation and style as main targets of the cure, also treating possible pornographic addiction and resulting conjugopathy when that was the case. The duration of the treatment spread between 4 months for those who have been diligent and more a year for those who are discouraged and have stopped many times. Reversal requires one to three years. Nineteen patients were dis-habituated from their conditioning, 3 are in progress, 13 have given up or disappeared from view.
3) Unusual masturbatory practice as an etiological factor in the diagnosis and treatment of sexual dysfunction in young men (2014) – One of the 4 case studies in this paper reports on a man with porn-induced sexual problems (low libido, fetishes, anorgasmia). The sexual intervention called for a 6-week abstinence from porn and masturbation. After 8 months the man reported increased sexual desire, successful sex and orgasm, and enjoying “good sexual practices. This is the first peer-reviewed chronicling of a recovery from porn-induced sexual dysfunctions. Excerpts from the paper, including the intervention
“When asked about masturbatory practices, he reported that in the past he had been masturbating vigorously and rapidly while watching pornography since adolescence. The pornography originally consisted mainly of zoophilia, and bondage, domination, sadism, and masochism, but he eventually got habituated to these materials and needed more hardcore pornography scenes, including transgender sex, orgies, and violent sex. He used to buy illegal pornographic movies on violent sex acts and rape and visualized those scenes in his imagination to function sexually with women. He gradually lost his desire and his ability to fantasize and decreased his masturbation frequency.”
Intervention:
In conjunction with weekly sessions with a sex therapist, the patient was instructed to avoid any exposure to sexually explicit material, including videos, newspapers, books, and internet pornography.
After 8 months, the patient reported experiencing successful orgasm and ejaculation. He renewed his relationship with that woman, and they gradually succeeded in enjoying good sexual practices.
4) How difficult is it to treat delayed ejaculation within a short-term psychosexual model? A case study comparison (2017) – A report on two “composite cases” illustrating the causes and treatments for delayed ejaculation (anorgasmia). “Patient B” represented several young men treated by the therapist. Interestingly, the paper states that Patient B’s “porn use had escalated into harder material”, “as is often the case”. The paper says that porn-related delayed ejaculation is not uncommon, and on the rise. The author calls for more research on porn’s effects of sexual functioning. Patient B’s delayed ejaculation was healed after 10 weeks of no porn. Excerpts:
The cases are composite cases taken from my work within the National Health Service in Croydon University Hospital, London. With the latter case (Patient B), it is important to note that the presentation reflects a number of young males who have been referred by their GPs with a similar diagnosis. Patient B is a 19-year-old who presented because he was unable to ejaculate via penetration. When he was 13, he was regularly accessing pornography sites either on his own through internet searches or via links that his friends sent him. He began masturbating every night while searching his phone for image…If he did not masturbate he was unable to sleep. The pornography he was using had escalated, as is often the case (see Hudson-Allez, 2010), into harder material (nothing illegal)…
Patient B was exposed to sexual imagery via pornography from the age of 12 and the pornography he was using had escalated to bondage and dominance by the age of 15.
The intervention:
We agreed that he would no longer use pornography to masturbate. This meant leaving his phone in a different room at night. We agreed that he would masturbate in a different way….
Patient B was able to achieve orgasm via penetration by the fifth session; the sessions are offered fortnightly in Croydon University Hospital so session five equates to approximately 10 weeks from consultation. He was happy and greatly relieved. In a three-month follow-up with Patient B, things were still going well.
Patient B is not an isolated case within the National Health Service (NHS) and in fact young men in general accessing psychosexual therapy, without their partners, speaks in itself to the stirrings of change.
This article therefore supports previous research that has linked masturbation style to sexual dysfunction and pornography to masturbation style. The article concludes by suggesting that the successes of psychosexual therapists in working with DE are rarely recorded in the academic literature, which has allowed the view of DE as a difficult disorder to treat remain largely unchallenged. The article calls for research into pornography usage and its effect on masturbation and genital desensitisation.
5) Situational Psychogenic Anejaculation: A Case Study (2014) – The details reveal a case of porn-induced anejaculation. The husband’s only sexual experience prior to marriage was frequent masturbation to pornography – where he was able to ejaculate. He also reported sexual intercourse as less arousing than masturbation to porn. The key piece of information is that “re-training” and psychotherapy failed to heal his anejaculation. When those interventions failed, therapists suggested a complete ban on masturbation to porn. Eventually this ban resulted in successful sexual intercourse and ejaculation with a partner for the first time in his life. A few excerpts:
A is a 33-year-old married male with heterosexual orientation, a professional from a middle socio-economic urban background. He has had no premarital sexual contacts. He watched pornography and masturbated frequently. His knowledge about sex and sexuality was adequate. Following his marriage, Mr. A described his libido as initially normal, but later reduced secondary to his ejaculatory difficulties. Despite thrusting movements for 30-45 minutes, he had never been able to ejaculate or achieve orgasm during penetrative sex with his wife.
What didn’t work:
Mr. A’s medications were rationalized; clomipramine and bupropion were discontinued, and sertraline was maintained at a dose of 150 mg per day. Therapy sessions with the couple were held weekly for the initial few months, following which they were spaced to fortnightly and later monthly. Specific suggestions including focusing on sexual sensations and concentrating on the sexual experience rather than ejaculation were used to help reduce performance anxiety and spectatoring. Since problems persisted despite these interventions, intensive sex therapy was considered.
The intervention – eventually they instituted a complete ban on masturbation (which means he continued to masturbate to porn during the above failed interventions):
A ban on any form of sexual activity was suggested. Progressive sensate focus exercises (initially non-genital and later genital) were initiated. Mr. A described an inability to experience the same degree of stimulation during penetrative sex as compared to that which he experienced during masturbation. Once the ban on masturbation was enforced, he reported an increased desire for sexual activity with his partner.
After an unspecified amount of time, the ban on masturbation to porn lead to success:
Meanwhile, Mr. A and his wife decided to go ahead with Assisted Reproductive Techniques (ART) and underwent two cycles of intrauterine insemination. During a practice session, Mr. A ejaculated for the first time, following which he has been able to ejaculate satisfactorily during a majority of the couple’s sexual interactions.
6) Pornography Induced Erectile Dysfunction Among Young Men (2019) – Abstract:
This paper explores the phenomenon of pornography induced erectile dysfunction (PIED), meaning sexual potency problems in men due to Internet pornography consumption. Empirical data from men who suffer from this condition have been collected. A combination of topical life history method (with qualitative asynchronous online narrative interviews) and personal online diaries has been employed. The data have been analyzed using theoretical interpretative analysis (according to McLuhan’s media theory), based on analytic induction. The empirical investigation indicates that there is a correlation between pornography consumption and erectile dysfunction that suggests causation.
The findings are based on 11 interviews along with two video diaries and three text diaries. The men are between the ages of 16 and 52; they report that an early introduction to pornography (usually during adolescence) is followed by daily consumption until a point is reached where extreme content (involving, for example, elements of violence) is needed to maintain arousal. A critical stage is reached when sexual arousal is exclusively associated with extreme and fast-paced pornography, rendering physical intercourse bland and uninteresting. This results in an inability to maintain an erection with a real-life partner, at which point the men embark on a “re-boot” process, giving up pornography. This has helped some of the men to regain their ability to achieve and sustain an erection.
Introduction to the results section, with the common intervention:
Having processed the data, I have noticed certain patterns and recurring themes, following a chronological narrative in all of the interviews. These are: Introduction. One is first introduced to pornography, usually before puberty. Building a habit. One begins to consume pornography regularly. Escalation. One turns to more “extreme” forms of pornography, content-wise, in order to achieve the same effects previously achieved through less “extreme” forms of pornography. Realization. One notices sexual potency problems believed to be caused by pornography use. “Re-boot” process. One tries to regulate pornography use or eliminate it completely in order to regain one’s sexual potency. The data from the interviews are presented based on the above outline.
The remaining studies are listed by date of publication:
The Dual Control Model – The Role Of Sexual Inhibition & Excitation In Sexual Arousal And Behavior (2007) – Newly rediscovered and very convincing. In an experiment employing video porn, 50% of the young men couldn’t become aroused or achieve erections with porn (average age was 29). The shocked researchers discovered that the men’s erectile dysfunction was,
“related to high levels of exposure to and experience with sexually explicit materials.“
The men experiencing erectile dysfunction had spent a considerable amount of time in bars and bathhouses where porn was “omnipresent,” and “continuously playing“. The researchers stated:
“Conversations with the subjects reinforced our idea that in some of them a high exposure to erotica seemed to have resulted in a lower responsivity to “vanilla sex” erotica and an increased need for novelty and variation, in some cases combined with a need for very specific types of stimuli in order to get aroused.”
Clinical encounters with internet pornography (2008) – Comprehensive paper, with four clinical cases, written by a psychiatrist who became aware of the negative effects internet porn was having on some of his male patients. The excerpt below describes a 31 year old man who escalated into extreme porn and developed porn-induced sexual tastes and sexual problems. This is one of the first peer-reviewed papers to depict porn use leading to tolerance, escalation, and sexual dysfunctions:
A 31-year-old male in analytic psychotherapy for mixed anxiety problems reported that he was experiencing difficulty becoming sexually aroused by his current partner. After much discussion about the woman, their relationship, possible latent conflicts or repressed emotional content (without arriving at a satisfactory explanation for his complaint), he provided the detail that he was relying on a particular fantasy to become aroused. Somewhat chagrined, he described a “scene” of an orgy involving several men and women that he had found on an Internet pornography site that had caught his fancy and become one of his favorites.
Over the course of several sessions, he elaborated upon his use of Internet pornography, an activity in which he had engaged sporadically since his mid-20s. Relevant details about his use and the effects over time included clear descriptions of an increasing reliance on viewing and then recalling pornographic images in order to become sexually aroused. He also described the development of a “tolerance” to the arousing effects of any particular material after a period of time, which was followed by a search for new material with which he could achieve the prior, desired level of sexual arousal.
As we reviewed his use of pornography, it became evident that the arousal problems with his current partner coincided with use of pornography, whereas his “tolerance” to the stimulating effects of particular material occurred whether or not he was involved with a partner at the time or was simply using pornography for masturbation. His anxiety about sexual performance contributed to his reliance on viewing pornography. Unaware that the use itself had become problematic, he had interpreted his waning sexual interest in a partner to mean that she was not right for him, and had not had a relationship of greater than two months’ duration in over seven years, exchanging one partner for another just as he might change websites.
He also noted that he now could be aroused by pornographic material that he once had no interest in using. For example, he noted that five years ago he had little interest in viewing images of anal intercourse but now found such material stimulating. Similarly, material that he described as “edgier,” by which he meant “almost violent or coercive,” was something that now elicited a sexual response from him, whereas such material had been of no interest and was even off-putting. With some of these new subjects, he found himself anxious and uncomfortable even as he would become aroused.
Exploring the Relationship Between Erotic Disruption During the Latency Period and the Use of Sexually Explicit Material, Online Sexual Behaviors, and Sexual Dysfunctions in Young Adulthood (2009) – Study examined correlations between current porn use (sexually explicit material – SEM) and sexual dysfunctions, and porn use during “latency period” (ages 6-12) and sexual dysfunctions. The average age of participants was 22. While current porn use correlated with sexual dysfunctions, porn use during latency (ages 6-12) had an even stronger correlation with sexual dysfunctions. A few excerpts:
Findings suggested that latency erotic disruption by way of sexually explicit material (SEM) and/or child sexual abuse may be associated to adult online sexual behaviors.
Furthermore, results demonstrated that latency SEM exposure was a significant predictor of adult sexual dysfunctions.
Use of pornography in a random sample of Norwegian heterosexual couples (2009) – Porn use was correlated with more sexual dysfunctions in the man and negative self perception in the female. The couples who did not use porn had no sexual dysfunctions. A few excerpts from the study:
In couples where only one partner used pornography, we found more problems related to arousal (male) and negative (female) self-perception.
In those couples where one partner used pornography there was a permissive erotic climate. At the same time, these couples seemed to have more dysfunctions.
The couples who did not use pornography… may be considered more traditional in relation to the theory of sexual scripts. At the same time, they did not seem to have any dysfunctions.
Couples who both reported pornography use grouped to the positive pole on the ‘‘Erotic climate’’ function and somewhat to the negative pole on the ‘‘Dysfunctions’’ function.
Cyber-porn dependence: voices of distress in an Italian internet self-help community (2009) – This study reports on a narrative analysis of two thousand messages written by 302 members of an Italian self-help group for cyberdependents (noallapornodipendenza). It sampled 400 messages from each year (2003–2007). Excerpts relevant to porn-induced sexual dysfunctions:
For many their condition is reminiscent of an addicted escalation with new levels of tolerance. Many of them in fact search for increasingly more explicit, bizarre and violent images, bestiality included….
Many members complain about increased impotence and lack of ejaculation, feeling in their real life like “a dead man walking” (“vivalavita” #5014). The following example concretizes their perceptions (“sul” #4411)….
Many participants stated that they usually spend hours looking at and collecting pictures and movies holding their erect penis in their hand, unable to ejaculate, waiting for the ultimate, extreme image to release the tension. For many the final ejaculation puts an end to their torture (supplizio) (“incercadiliberta” #5026)…
Problems in heterosexual relations are more than frequent. People complain they have erection problems, lack of sexual relations with their spouses, lack of interest in sexual intercourse, feeling like a person who has eaten hot, spicy food, and consequently cannot eat ordinary food. In many cases, as also reported by spouses of cyber dependents, there are indications of male orgasmic disorder with the inability to ejaculate during intercourse. This sense of desensitization in sexual relationships is well expressed in the following passage (“vivaleiene” #6019):
Last week I had an intimate relation with my girlfriend; nothing bad at all, despite the fact after the first kiss I didn’t feel any sensation. We didn’t finish the copulation because I didn’t want to.
Many participants expressed their real interest in “chatting on line” or “telematic contact” instead of physical touch, and a pervasive and unpleasant presence of pornographic flashbacks in their mind, during sleep and during sexual intercourse.
As stressed, the claim of a real sexual dysfunction is echoed by many testimonials from female partners. But also forms of collusion and contamination appear in these narratives. Here are a few of the most striking comments of these female partners…
Most of the messages sent to the Italian self help group do indicate the presence of pathology by those participants, according to the model of salience (in real life), mood modification, tolerance, withdrawal symptoms and interpersonal conflict, a diagnostic model developed by Griffiths (2004)….
Brain Structure and Functional Connectivity Associated With Pornography Consumption: The Brain on Porn (2014) – A Max Planck study which found 3 significant addiction-related brain changes correlating with the amount of porn consumed. It also found that the more porn consumed the less reward circuit activity in response to brief exposure (.530 second) to vanilla porn. In a 2014 article lead author Simone Kühn said:
“We assume that subjects with a high porn consumption need increasing stimulation to receive the same amount of reward. That could mean that regular consumption of pornography more or less wears out your reward system. That would fit perfectly the hypothesis that their reward systems need growing stimulation.”
A more technical description of this study from a review of the literature by Kuhn & Gallinat – Neurobiological Basis of Hypersexuality (2016).
“The more hours participants reported consuming pornography, the smaller the BOLD response in left putamen in response to sexual images. Moreover, we found that more hours spent watching pornography was associated with smaller gray matter volume in the striatum, more precisely in the right caudate reaching into the ventral putamen. We speculate that the brain structural volume deficit may reflect the results of tolerance after desensitization to sexual stimuli.”
Neural Correlates of Sexual Cue Reactivity in Individuals with and without Compulsive Sexual Behaviours (2014) – This fMRI study by Cambridge University found sensitization in porn addicts which mirrored sensitization in drug addicts. It also found that porn addicts fit the accepted addiction model of wanting “it” more, but not liking “it” more. The researchers also reported that 60% of subjects (average age: 25) had difficulty achieving erections/arousal with real partners as a result of using porn, yet could achieve erections with porn. From the study (“CSB” is compulsive sexual behaviours):
“CSB subjects reported that as a result of excessive use of sexually explicit materials…..[they] experienced diminished libido or erectile function specifically in physical relationships with women (although not in relationship to the sexually explicit material)”
“Compared to healthy volunteers, CSB subjects had greater subjective sexual desire or wanting to explicit cues and had greater liking scores to erotic cues, thus demonstrating a dissociation between wanting and liking. CSB subjects also had greater impairments of sexual arousal and erectile difficulties in intimate relationships but not with sexually explicit materials highlighting that the enhanced desire scores were specific to the explicit cues and not generalized heightened sexual desire.”
Adolescents and web porn: a new era of sexuality (2015) – This Italian study analyzed the effects of Internet porn on high school seniors, co-authored by urology professor Carlo Foresta, president of the Italian Society of Reproductive Pathophysiology. The most interesting finding is that 16% of those who consume porn more than once a week report abnormally low sexual desire compared with 0% in non-consumers (and 6% for those who consume less than once a week). From the study:
“21.9% define it as habitual, 10% report that it reduces sexual interest towards potential real-life partners, and the remaining, 9.1% report a kind of addiction. In addition, 19% of overall pornography consumers report an abnormal sexual response, while the percentage rose to 25.1% among regular consumers.”
Patient Characteristics by Type of Hypersexuality Referral: A Quantitative Chart Review of 115 Consecutive Male Cases (2015) – A study on men (average age 41.5) with hypersexuality disorders, such as paraphilias, chronic masturbation or adultery. 27 of the men were classified as “avoidant masturbators,” meaning they masturbated (typically with porn use) one or more hours per day, or more than 7 hours per week. 71% of the men who chronically masturbated to porn reported sexual functioning problems, with 33% reporting delayed ejaculation (a precursor to porn-induced ED).
Men’s Sexual Life and Repeated Exposure to Pornography. A New Issue? (2015) – Excerpts:
Mental health specialists should take in consideration the possible effects of pornography consumption on men sexual behaviors, men sexual difficulties and other attitudes related to sexuality. In the long term pornography seems to create sexual dysfunctions, especially the individual’s inability to reach an orgasm with his partner. Someone who spends most of his sexual life masturbating while watching porn engages his brain in rewiring its natural sexual sets (Doidge, 2007) so that it will soon need visual stimulation to achieve an orgasm.
Many different symptoms of porn consumption, such as the need to involve a partner in watching porn, the difficulty in reaching orgasm, the need for porn images in order to ejaculate turn into sexual problems. These sexual behaviors may go on for months or years and it may be mentally and bodily associated with the erectile dysfunction, although it is not an organic dysfunction. Because of this confusion, which generates embarrassment, shame and denial, lots of men refuse to encounter a specialist
Pornography offers a very simple alternative to obtain pleasure without implying other factors that were involved in human’s sexuality along the history of mankind. The brain develops an alternative path for sexuality which excludes “the other real person” from the equation. Furthermore, pornography consumption in a long term makes men more prone to difficulties in obtaining an erection in a presence of their partners.
Masturbation and Pornography Use Among Coupled Heterosexual Men With Decreased Sexual Desire: How Many Roles of Masturbation? (2015) – Masturbating to porn was related with decreased sexual desire and low relationship intimacy. Excerpts:
Among men who masturbated frequently, 70% used pornography at least once a week. A multivariate assessment showed that sexual boredom, frequent pornography use, and low relationship intimacy significantly increased the odds of reporting frequent masturbation among coupled men with decreased sexual desire.
Among men [with decreased sexual desire] who used pornography at least once a week [in 2011], 26.1% reported that they were unable to control their pornography use. In addition, 26.7% of men reported that their use of pornography negatively affected their partnered sex and 21.1% claimed to have attempted to stop using pornography.
Erectile Dysfunction, Boredom, and Hypersexuality among Coupled Men from Two European Countries (2015) – Survey reported a strong correlation between erectile dysfunction and measures of hypersexuality (Compulsive Sexual Behavior Disorder). The study omitted correlation data between erectile functioning and pornography use, but noted a significant correlation. An excerpt:
Among Croatian and German men, hypersexuality was significantly correlated with proneness to sexual boredom and more problems with erectile function.
An Online Assessment of Personality, Psychological, and Sexuality Trait Variables Associated with Self-Reported Hypersexual Behavior (2015) – Survey reported a common theme found in several other studies listed here: Porn/sex addicts report greater arousabilty (cravings related to their addiction) combined with poorer sexual function (fear of experiencing erectile dysfunction).
“Hypersexual” behavior represents a perceived inability to control one’s sexual behavior. To investigate hypersexual behavior, an international sample of 510 self-identified heterosexual, bisexual, and homosexual men and women completed an anonymous online self-report questionnaire battery.
Thus, the data indicated that hypersexual behavior is more common for males, and those who report being younger in age, more easily sexually excited, more sexually inhibited due to the threat of performance failure, less sexually inhibited due to the threat of performance consequences, and more impulsive, anxious, and depressed
Online sexual activities: An exploratory study of problematic and non-problematic usage patterns in a sample of men (2016) – This Belgian study from a leading research university found problematic Internet porn use was associated with reduced erectile function and reduced overall sexual satisfaction. Yet problematic porn users experienced greater cravings. The study appears to report escalation, as 49% of the men viewed porn that “was not previously interesting to them or that they considered disgusting.” (See studies reporting habituation/desensitization to porn and escalation of porn use) Excerpts:
“This study is the first to directly investigate the relationships between sexual dysfunctions and problematic involvement in OSAs. Results indicated that higher sexual desire, lower overall sexual satisfaction, and lower erectile function were associated with problematic OSAs (online sexual activities).
The effects of sexually explicit material use on romantic relationship dynamics (2016) – As with many other studies, solitary porn users report poorer relationship and sexual satisfaction. Employing the Pornography Consumption Effect Scale (PCES), the study found that higher porn use was related to poorer sexual function, more sexual problems, and a “worse sex life”. An excerpt describing the correlation between the PCES “Negative Effects” on “Sex Life” questions and frequency of porn use:
There were no significant differences for the Negative Effect Dimension PCES across the frequency of sexually explicit material use; however, there were significant differences on the Sex Life subscale where High Frequency Porn Users reported greater negative effects than Low Frequency Porn Users.
Associative pathways between pornography consumption and reduced sexual satisfaction (2017) While it links porn use to lower sexual satisfaction, it also reported that frequency of porn use was related to a preference (or need?) for porn over people to achieve sexual arousal. An excerpt:
Finally, we found that frequency of pornography consumption was also directly related to a relative preference for pornographic rather than partnered sexual excitement. Participants in the present study primarily consumed pornography for masturbation. Thus, this finding could be indicative of a masturbatory conditioning effect (Cline, 1994; Malamuth, 1981; Wright, 2011). The more frequently pornography is used as an arousal tool for masturbation, the more an individual may become conditioned to pornographic as opposed to other sources of sexual arousal.
“I think it has been a negative influence in many ways but at the same time I can’t stop using it”: Self-identified problematic pornography use among a sample of young Australians (2017) – Online survey of Australians, aged 15-29. Those who had ever viewed pornography (n=856) were asked in an open-ended question: ‘How has pornography influenced your life?’.
Among participants who responded to the open-ended question (n=718), problematic usage was self-identified by 88 respondents. Male participants who reported problematic usage of pornography highlighted effects in three areas: on sexual function, arousal and relationships. Responses included “I think it has been a negative influence in many ways but at the same time I can’t stop using it” (Male, Aged 18–19). Some female participants also reported problematic usage, with many of these reporting negative feelings like guilt and shame, impact on sexual desire and compulsions relating to their use of pornography. For example as one female participant suggested; “It makes me feel guilty, and I’m trying to stop. I don’t like how I feel that I need it to get myself going, it’s not healthy.” (Female, Aged 18–19)
Organic and psychogenic causes of sexual dysfunction in young men (2017) – A narrative review, with a section called “Role of Pornography in Delayed Ejaculation (DE)”. An excerpt from this section:
Role of Pornography in DE
Over the last decade, a large increase in the prevalence and accessibility of Internet pornography has provided increased causes of DE associated with Althof’s second and third theory. Reports from 2008 found on average 14.4% of boys were exposed to pornography before the age of 13 and 5.2% of people viewed pornography at least daily.76 A 2016 study revealed that these values had both increased to 48.7% and 13.2%, respectively.76 An earlier age of first pornographic exposure contributes to DE through its relationship with patients exhibiting CSB.
Voon et al. found that young men with CSB had viewed sexually explicit material at an earlier age than their age-controlled healthy peers.75 As previously mentioned, young men with CSB can fall victim to Althof’s third theory of DE and preferentially choose masturbation over partnered sex due to a lack of arousal in relationships. An increased number of men watching pornographic material daily also contributes to DE through Althof’s third theory.
In a study of 487 male college students, Sun et al. found associations between the use of pornography and a decreased self-reported enjoyment of sexually intimate behaviors with real-life partners.76 These individuals are at an elevated risk of preferentially choosing masturbation over sexual encounters, as demonstrated in a case report by Park et al. A 20-year-old enlisted male presented with difficulty achieving orgasm with his fiancée for the previous six months. A detailed sexual history revealed that the patient relied on Internet pornography and use of a sex toy described as a “fake vagina” to masturbate while deployed. Over time, he required content of an increasingly graphic or fetish nature to orgasm. He admitted that he found his fiancée attractive but preferred the feeling of his toy because he found it more stimulating that real intercourse.77
An increase in the accessibility of Internet pornography places younger men at risk of developing DE through Althof’s second theory, as demonstrated in the following case report: Bronner et al. interviewed a 35-year-old healthy man presenting with complaints of no desire to have sex with his girlfriend despite being mentally and sexually attracted to her. A detailed sexual history revealed that this scenario had happened with the past 20 women he tried to date. He reported extensive use of pornography since adolescence that initially consisted of zoophilia, bondage, sadism, and masochism, but eventually progressed to transgender sex, orgies, and violent sex. He would visualize the pornographic scenes in his imagination to function sexually with women, but that gradually stopped working.74
The gap between the patient’s pornographic fantasies and real life became too large, causing a loss of desire. According to Althof, this will present as DE in some patients.73 This recurring theme of requiring pornographic content of an increasingly graphic or fetish nature to orgasm is defined by Park et al. as hyperactivity. As a man sensitizes his sexual arousal to pornography, sex in real life no longer activates the proper neurological pathways to ejaculate (or produce sustained erections in the case of ED).77
Sexual Dysfunctions in the Internet Era (2018) – Excerpts:
Low sexual desire, reduced satisfaction in sexual intercourse, and erectile dysfunction (ED) are increasingly common in young population. In an Italian study from 2013, up to 25% of subjects suffering from ED were under the age of 40 [1], and in a similar study published in 2014, more than half of Canadian sexually experienced men between the age of 16 and 21 suffered from some kind of sexual disorder [2]. At the same time, prevalence of unhealthy lifestyles associated with organic ED has not changed significantly or has decreased in the last decades, suggesting that psychogenic ED is on the rise [3].
The DSM-IV-TR defines some behaviors with hedonic qualities, such as gambling, shopping, sexual behaviors, Internet use, and video game use, as “impulse control disorders not elsewhere classified”—although these are often described as behavioral addictions [4]. Recent investigation has suggested the role of behavioral addiction in sexual dysfunctions: alterations in neurobiological pathways involved in sexual response might be a consequence of repeated, supernormal stimuli of various origins.
Among behavioral addictions, problematic Internet use and online pornography consumption are often cited as possible risk factors for sexual dysfunction, often with no definite boundary between the two phenomena. Online users are attracted to Internet pornography because of its anonymity, affordability, and accessibility, and in many cases its usage could lead users through a cybersex addiction: in these cases, users are more likely to forget the “evolutionary” role of sex, finding more excitement in self-selected sexually explicit material than in intercourse.
In literature, researchers are discordant about positive and negative function of online pornography. From the negative perspective, it represents the principal cause of compulsive masturbatory behavior, cybersex addiction, and even erectile dysfunction.
While the Grubbs paper consistently downplays the correlations between higher pornography use and poorer erections, correlations were reported in all 3 groups – especially for sample 3, which was the most relevant sample as it was the largest sample and averaged higher levels of porn use. Most importantly, this sample’s age range is the most likely to report PIED. Not surprisingly, sample 3 had the strongest correlation between higher levels of porn use and poorer erectile functioning (–0.37). Below are the 3 groups, with their average daily minutes of porn viewing and the correlations between erectile functioning amount of use:
- Sample 1 (147 men): average age 19.8 – Averaged 22 minutes of porn/day. (–0.18)
- Sample 2 (297 men): average age 46.5 – Averaged 13 minutes of porn/day. (–0.05)
- Sample 3 (433 men): average age 33.5 – Averaged 45 minutes of porn/day. (–0.37)
Fairly straightforward results: the sample that used the most porn (#3) had the strongest correlation between greater porn use and poorer erections, while the group that use the least (#2) had the weakest correlation between greater porn use and poorer erections.
Grubbs also correlated porn addiction scores with erectile functioning. The results reveal that even in subjects with relatively healthy erectile functioning, porn addiction was significantly related to poorer erections (–0.20 to –0.33). As before, the strongest correlation between porn addiction and poorer erections (–0.33) occurred in Grubbs’s largest sample, and the sample of an average age most likely to report porn-induced ED: sample 3, average age: 33.5 (433 subjects).
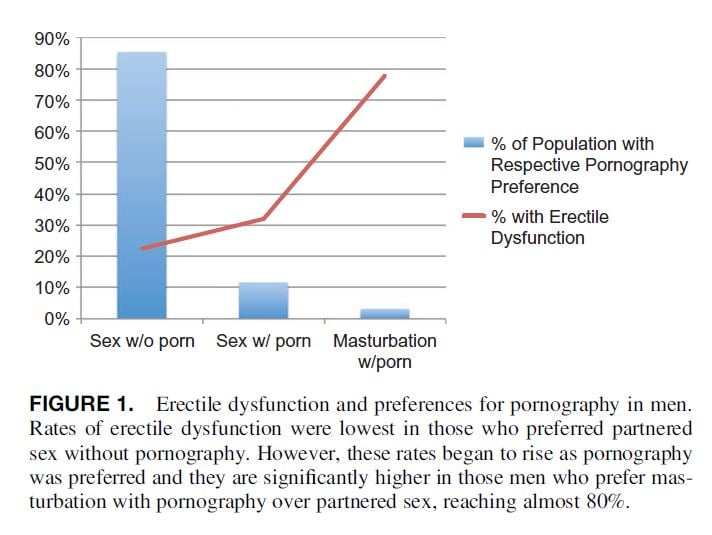
Survey of Sexual Function and Pornography (2019) – In this study, researchers looked for a link between ED and indices of pornography addiction using a “craving” questionnaire. While no such link turned up (perhaps because users don’t accurately assess their degree of “craving” until they attempt to quit using), some other interesting correlations appeared in their results. Excerpts:
Rates of erectile dysfunction were lowest in those [men] preferring partnered sex without pornography (22.3%) and increased significantly when pornography was preferred over partnered sex (78%).
…Pornography and sexual dysfunction are common among young people.
…Those [men] who used on an almost daily basis or more had ED rates of 44% (12/27) compared to 22% (47/213) for those more “casual” users (≤5x/week), reaching significance on univariate analysis (p=0.017). It may be that volume does play a role to some extent.
…The proposed pathophysiology of PIED seems plausible and is based on a variety of researchers work and not a small collection of researchers that might be swayed by an ethical bias. Also supporting the “causation” side of the argument are reports of men regaining normal sexual function after discontinuation of excessive pornography use.
…Only prospective studies will be able to definitively solve the question of causation or association, including interventional studies evaluating the success of abstention in treating ED in heavy pornography users. Additional populations that warrant special consideration include adolescents. There has been concern raised that early exposure to graphic sexual material may affect normal development. The rate of teenagers being exposed to pornography before the age of 13 has gone up three fold over the last decade, and now hovers around 50%.
Sexual Dysfunction in the New Father: Sexual Intimacy Issues (2018) – This chapter from a new medical textbook entitled Paternal Postnatal Psychiatric Illnesses addresses porn’s impact on the sexual function of a new father. This page contains screenshots of relevant excerpts from the chapter.
Prevalence, Patterns and Self-Perceived Effects of Pornography Consumption in Polish University Students: A Cross-Sectional Study (2019) Large study (n = 6463) on male & female college students (median age 22) reports relatively high levels of porn addiction (15%), escalation of porn use (tolerance), withdrawal symptoms, and porn-related sexual & relationship problems. Relevant excerpts:
The most common self-perceived adverse effects of pornography use included: the need for longer stimulation (12.0%) and more sexual stimuli (17.6%) to reach orgasm, and a decrease in sexual satisfaction (24.5%)…
The present study also suggests that earlier exposure may be associated with potential desensitization to sexual stimuli as indicated by a need for longer stimulation and more sexual stimuli required to reach orgasm when consuming explicit material, and overall decrease in sexual satisfaction…
Various changes of pattern of pornography use occurring in the course of the exposure period were reported: switching to a novel genre of explicit material (46.0%), use of materials that do not match sexual orientation (60.9%) and need to use more extreme (violent) material (32.0%)…
Sexual and reproductive health and rights in Sweden 2017 (2019) – A 2017 survey by The Swedish Public Health Authority contains a section discussing their findings on pornography. relevant here, greater pornography use was related to poorer sexual health and decreased sexual dissatisfaction. Excerpts:
Forty-one percent of men aged 16 to 29 are frequent users of pornography, i.e. they consume pornography on a daily basis or almost on a daily basis. The corresponding percent among women is 3 percent. Our results also show an association between frequent pornography consumption and poorer sexual health, and an association with transactional sex, too high expectations of one’s sexual performance, and dissatisfaction with one’s sex life. Almost half of the population state that their pornography consumption does not affect their sex life, while a third do not know if it affects it or not. A small percentage of both women and men say their pornography use has a negative effect on their sex life. It was more common among men with higher education to regularly use pornography compared to men with lower education.
There is a need for more knowledge on the link between pornography consumption and health. An important preventive piece is to discuss the negative consequences of pornography with boys and young men, and school is a natural place to do this.
Link to PDF of the chapter in “Introduction to Psychosexual Medicine (2019)” – White, Catherine. Internet Pornography – Addiction or Sexual Dysfunction. Introduction to Psychosexual Medicine (2019)